
Indirect IM (also called impression management by association) refers to “behaviors undertaken by individuals at work through associations with other colleagues to create favorable impressions of themselves” ( Cialdini and Richardson, 1980). Direct IM refers to “individuals self-promoting their own achievements and success” ( Tal-Or and Drukman, 2010). A better understanding of the mechanism linking IM and the career-related outcomes requires distinguishing between different IM types, as different IM mechanisms might lead to different career outcomes.įirst, IM may depend on the mechanism used, creating favorable impressions through two different types: direct and indirect IM. In this vein, individuals using IM have higher chances of getting positive job interview ratings ( Amaral et al., 2019).
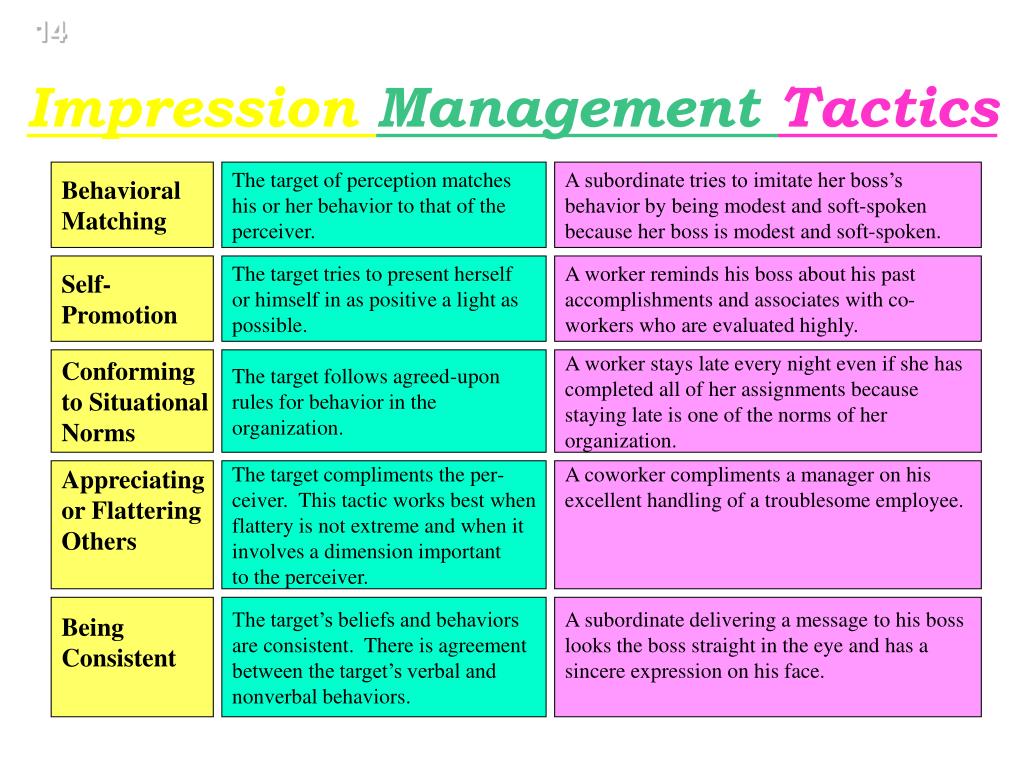
For example, developing a resume and showing daily achievements online are unavoidable tools to enhance our career ( El Ouirdi et al., 2015). Amongst other tools, IM has revolutionized career development, offering competitive and sustainable career opportunities ( Villeda and McCamey, 2019). IM is of primary importance for individuals, since the impressions they make on others influences how others perceive and treat them ( Bozeman and Kacmar, 1997 Gioaba and Krings, 2017). IM can be defined as the process by which “individuals attempt to control the impressions others form of them” ( Leary and Kowalski, 1990). In recent years, impression management (IM) has received renewed attention among scholars (e.g., Liu et al., 2019 Yang et al., 2021). This study thus provides evidence of the need to investigate and differentiate between the different types of IM and interaction modes for career-related outcomes, highlighting some research gaps and directions for future inquiry. The review shows that direct IM is more widely studied in the face-to-face than online interaction mode, while indirect IM is neglected in both interaction modes. online) in a career development perspective. indirect) and modes of interaction (face-to-face vs. Accordingly, this study presents the first systematic literature review that differentiates between types of IM (direct vs.

Indeed, recent developments suggest that online interactions now prevail over face-to-face interactions, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.

While most empirical studies focus on direct IM, individuals engage in both types of IM and interaction modes, particularly indirect IM in the online context.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
